Sony FE 400-800 mm f/6.3-8 G OSS
10. Autofocus and focus breathing
Autofocus
The autofocus of the Sony 400-800 mm was tested with the help of the Sony A6700, the Sony A7R IIIa and the Sony A7R V. In all these cases the performance of the mechanism was completely noiseless.When it comes to the speed, it was hardly very fast when we used the full range available. Running through the whole range and confirming the focus took about 0.6-0.8 of a second and it's worth reminding here that the mechanism didn't waver or oscillate during that process. The time didn't depend on the focal length used but you have to remember that the minimum focusing distance decreases with the increase of the focal length so the focus throw shortens accordingly.In case of the Sony FE 200-600 mm f/5.6-6.3 G OSS we also had a choice between different focusing ranges and the limit was set at 10 meters. My practice showed that it was a level a tad too high. I suppose similar remarks have reached Sony from other users as well and in the case of 400-800 mm they decided to make a very wise move. They offer ranges that intertwine. Here you deal with with a FULL mode, a range from the minimum distance to 10 meters and from 8 meters to infinity. It is a step forward compared to the 200-600 mm model but still the Sony lags behind its rivals that allow you to set ranges on your own via a dedicated device. It's a pity Sony doesn't include such an option e.g. in its camera bodies. Being their producer they don't have to offer additional devices after all.
Employing a limit from 8 meters to infinity makes the performance of the autofocus noticeably more efficient. In this case the whole operation, including the confirmation of the focus, takes no longer than about 0.3-0.4 of a second.
Please Support UsIf you enjoy our reviews and articles, and you want us to continue our work please, support our website by donating through PayPal. The funds are going to be used for paying our editorial team, renting servers, and equipping our testing studio; only that way we will be able to continue providing you interesting content for free. |
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
When it comes to the accuracy of the mechanism we put the camera along with the lens on a tripod in our studio so there were no real reasons to complain. The situation was a bit different outside but it didn't steem from the performance of the autofocus but the specificity of the parameters, used here. With the 800 mm focal length, such physical dimensions as the length and weight (the lens with the camera weighs over 3 kilograms) taking photo handheld even with optical stabilization switched on, is simply difficult. Vibrations and deflections are so pronounced that stabilization and autofocus mechanisms with a function of tracking for example an eye of a bird work on the borderline of their maximum efficiency, not always hitting where they should. The situation can be saved if you lean on the tree, a wall or a lamppost. As you can imagine, taking photos handheld in a longer period of time is really demanding.
As show photos below, the tested lens didn't have any distinct problems with front or back focus tendencies, no matter what body we employed.
| A7R IIIa, 400 mm, f/6.3 |
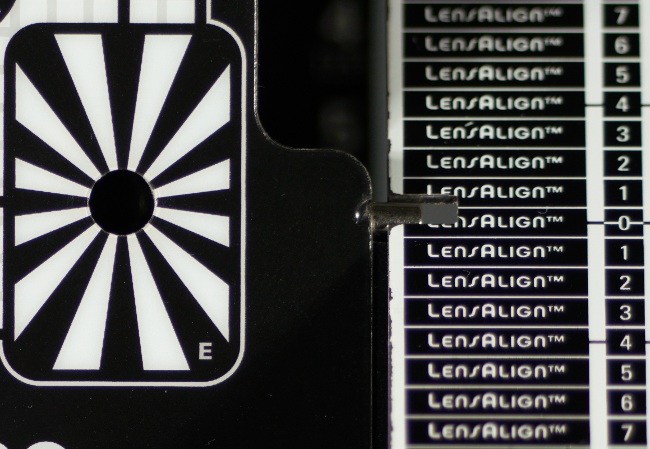 |
| A7R IIIa, 800 mm, f/8.0 |
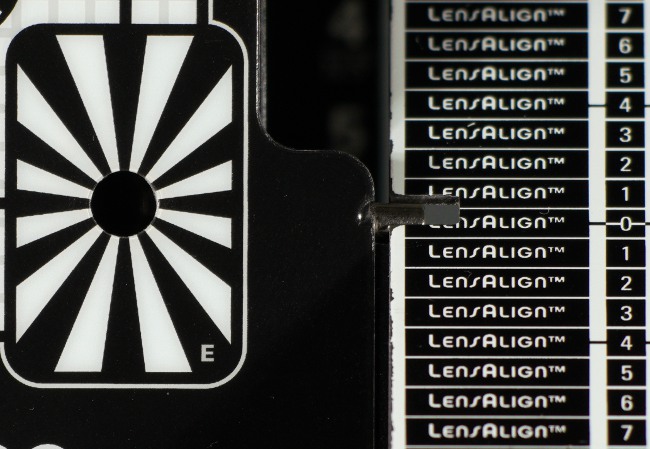 |
| A7R V, 400 mm, f/6.3 |
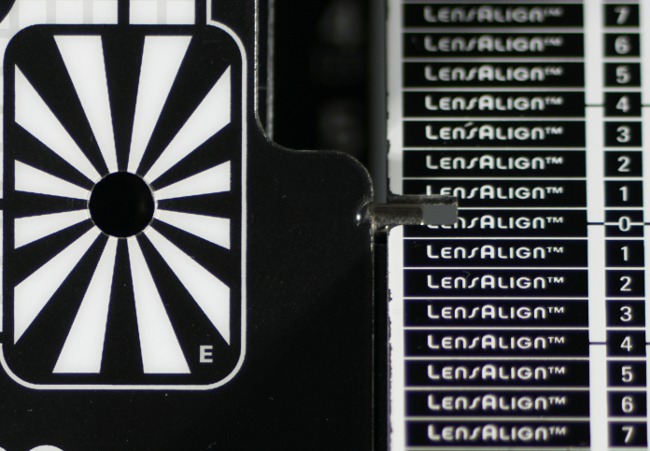 |
| A7R V, 800 mm, f/8.0 |
 |
Focus breathing
Focus breathing tests show reframing images as you oversharp them. We conduct the test by manually passing from the minimum focusing distance to infinity with the aperture stopped down; then we check how the field of view of the lens changed as a result.A frame change ranging from 0 to 5% we consider to be low. Between 5 and 10% you can speak about medium levels. Usually such values constitute also the maximum efficiency level of any breathing compensation algorithms, present in some bodies. Between 10 and 15% focus breathing is high, above 15% its level can be called very high.
The test video of the Sony lens is shown below: